Centralized Logging
Overview¶
The Enhanced Mule Logging Connector is also designed to support integration with centralized logging systems like Splunk or ELK.
Warning
Since RTF now supports custom log4j configuration, we're currently planning to remove the log sending automatic configuration from this connector (which is a bit of a "hack") and instead add that capability through Enhanced Mule Tools
This can be done by customizing the application log4j configuration to send logs in a protocol and format that the logging system to parse.
Typically the protocols used will be based on raw TCP or HTTP.
Regarding the format, while it's possible to create rules to parse the standard textual log patterns that is a time consuming and error-prone process, so instead the best practice is to send logs in JSON format that can be easily parsed by most logging systems.
While settings up this integration is typically a straightforward configuration using out-of-the-box log4j capabilities, this is much more complicated to do in mulesoft because of technical limitations:
- Out-of-the-box JSON layouts aren't compatible with mule 4
- Cloudhub requires special configuration to allow custom log4j configurations
- RTF only supports custom log4j configuration starting from version 1.13.91 ( released nov 22)
To solve those issues, Enhanced Mule Logging provides it's own JSON layout that is compatible with mule 4, and provides support for automated configuration of log4j at runtime which should bypass those limitations.
The downside of the automated configuration is that future changes in runtimes might break this feature if there are incompatibilities in newer log4j versions used by the runtime.
Enabling or disabling automated log4j is very easy to do so you could start by using that first, and if it doesn't work (or stops working),
you can easily switch to the manual configuration.
Configuration¶
In order to enable automated configuration, just set Send Logs > Enabled to true (it is off course recommended to use a property so that you can change this via runtime manager).
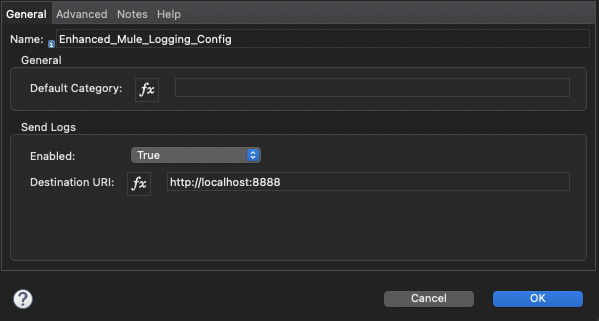
And then just set the the endpoint address:
For TCP endpoints use the uri pattern tcp://[hostname]:[port]. ie: tcp://localhost:5555
For HTTP endpoints type in an http:// or https:// URI. ie: https://myelkserver.example.com:8888
For manual configuration, you need to first add the package org.mule.extension.enhanced.mule.logging.jsonlayout to your
log4j2.xml configuration:
Then add the appropriate appender to your configuration file, using the EMJsonLayout layout.
For example to send logs via HTTP:
<Configuration packages="org.mule.extension.enhanced.mule.logging.jsonlayout">
<Appenders>
<Http name="Http" url="https://localhost:9200/test/log4j/">
<EMJsonLayout/>
</Http>
</Appenders>
</Configuration>
If your application is deployed in Cloudhub, don't forget to follow the instructions on this page: https://docs.mulesoft.com/cloudhub-1/custom-log-appender
Or for RTF (if you're using version 1.13.91 or greater follow those instructions: https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-fabric/1.13/use-log4j-appender
If you're using an older version of RTF then you can't configure log4j and instead will need to use the more limited log forwarding capabilities documented here: https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-fabric/1.0/configure-log-forwarding